In the world of AWS storage services, understanding the nuances between Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Storage) and Amazon EFS (Elastic File System) is crucial. Let's delve into their definitions, characteristics, use cases, and a comparative analysis to grasp their functionalities better.
EBS (Elastic Blog Store)
Amazon EBS, known as Elastic Block Store, is designed for exclusive use with EC2 instances. Acting as a block-level storage service, EBS offers high performance, making it ideal for various applications, including databases and software development.

EBS stores files in multiple volumes called blocks, which act as separate hard drives, and this storage is not accessible via the internet. EBS is similar to a hard-drive connected to a physical device and this storage can be attached or detached at any time.
EFS (Elastic File System)
Amazon EFS, or Elastic File System, provides shared elastic file storage with virtually unlimited scalability. Managed by AWS, EFS offers automatic scalability, ensuring users only pay for the storage they use. Its unique feature of scalability on-the-fly makes it stand out, especially for fluctuating workloads.
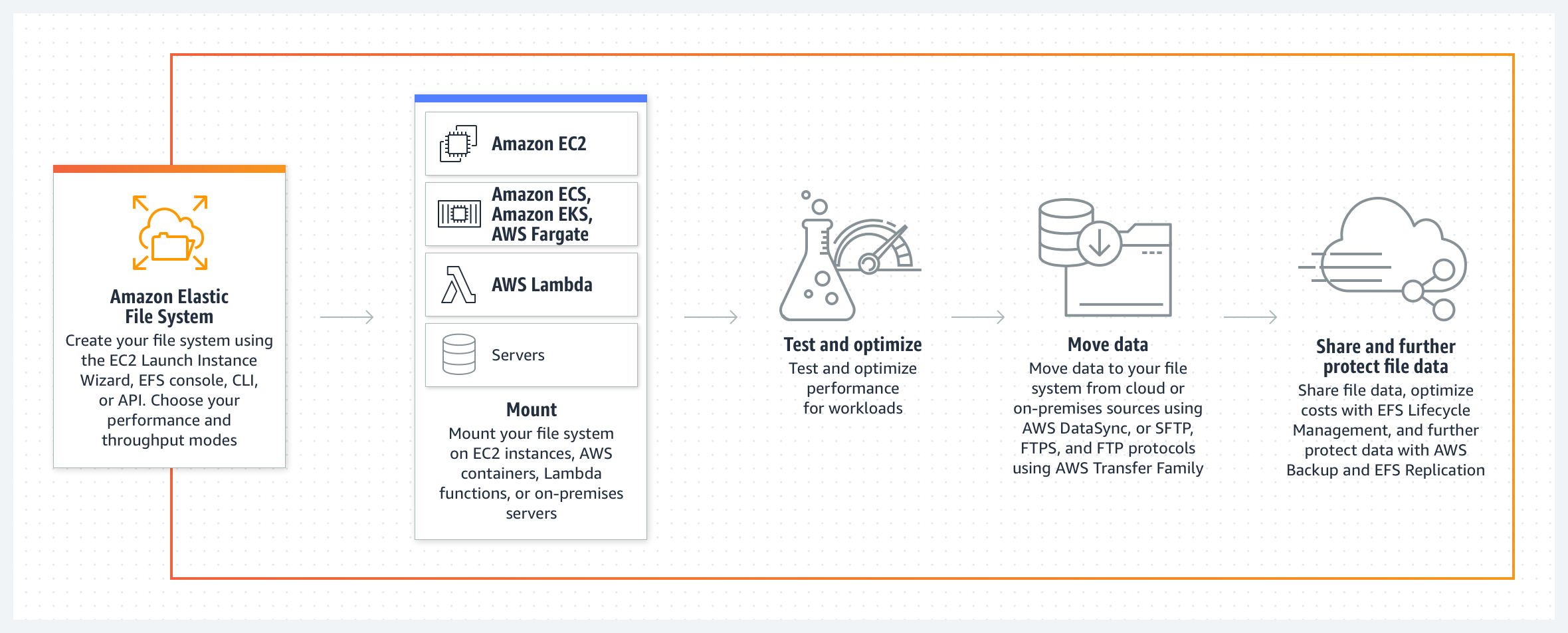
One of the most prominent features of EFS that separates it from all other storage is that the IOPS rate in EFS is inversely proportional to the size of data. For example, if the size of data is less, then the performance and IOPS rate might be not much significant but when used more heavily, EFS can offer as much as 10 GB/sec along with 500,000 IOPS.
Use Cases:
Amazon EBS: Suited for software testing and development, business continuity, enterprise-wide applications, and transactional databases.
Amazon EFS: Ideal for lift-and-shift application support, analytics for big data, web server support, and application development/testing.
Comparison based on Characteristics:
Storage Type:
EBS: Block-level
EFS: File-level
Availability:
EBS: Directly attached
EFS: Highly durable and available
Durability:
EBS: Offers 20 times more reliability
EFS: Highly durable
Performance:
EBS: Offers baseline performance
EFS: Supports up to 7000 file system operations per second
Data Access:
EBS: Accessible by a single EC2 instance
EFS: Supports concurrent access by multiple EC2 instances
Data Stored:
EBS: Data remains in the same availability zone
EFS: Data stays within the same region
Managed Service:
EBS: Requires patching and maintenance
EFS: Fully managed
File Size Limitation:
EBS: No file size limit
EFS: Maximum file size up to 47.9TiB
Encryption:
- Both support encryption using AWS KMS and AES 256-bit Encryption standards
Cost Savings:
EBS: Requires fixed volume attachment
EFS: Charges based on usage

In conclusion, both Amazon EBS and Amazon EFS serve unique purposes in the AWS ecosystem. While EBS offers high performance and reliability for specific use cases, EFS provides scalable, shared storage ideal for fluctuating workloads. Understanding their differences enables users to choose the most suitable option based on their requirements, ultimately optimizing their AWS infrastructure.